Global warming, the long-term rise in Earth’s average surface temperature, has become a critical issue impacting our world. Global warming directly results from CO2, methane, and nitrous oxide emissions, along with the release of various harmful gases into the Earth’s atmosphere. Understanding the complex and different ways global warming influences Earth’s climate is essential for developing mitigation strategies and fostering resilience in communities worldwide.
This article talks about various effects of global warming on Earth’s climate, examining changes in weather patterns, oceanic conditions, ecosystems, and the frequency of extreme weather events.
Changes in Weather Patterns
One of the most immediate and noticeable impacts of global warming is the changes in weather patterns. The increase in greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O) traps more heat in the Earth’s atmosphere, leading to a rise in global temperatures. This warming effect disrupts traditional weather patterns in several ways:
Temperature Extremes: As the global temperature rises, many regions experience more frequent and intense heat waves. These temperature extremes pose significant risks to human health, agriculture, and natural ecosystems.
Altered Precipitation Patterns: Global warming affects the hydrological cycle, leading to changes in precipitation patterns. Some areas may experience increased rainfall and flooding, while others face prolonged droughts.
Shift in Weather Systems: The warming of the atmosphere influences large-scale weather systems such as the jet stream and monsoons. These shifts can result in more erratic and unpredictable weather, affecting agricultural productivity and water resources.
Oceanic Changes
Oceans play a crucial role in regulating the global climate, absorbing about 93% of the excess heat generated by greenhouse gases. However, this absorption leads to several detrimental effects on oceanic conditions:
Rising Sea Levels: As global temperatures rise, polar ice caps and glaciers melt, contributing to sea level rise. This rise in sea levels will pose a threat to coastal communities, leading to increased flooding, erosion, and the displacement of millions of people. Low-lying island nations such as the Maldives are particularly vulnerable to these changes.
Ocean Acidification: Oceans absorb approximately 30% of the CO2 emitted by human activities. This alters the chemistry of seawater, resulting in ocean acidification. The increase in acidity has adverse effects on marine life, particularly organisms with calcium carbonate shells or skeletons, such as corals, molluscs, and certain plankton species.
Coral reefs, which support a majority of marine biodiversity, are especially at risk, with widespread bleaching events becoming more frequent.
Disruption of Ocean Currents:
Global warming can also impact ocean currents, which are important in distributing heat and nutrients around the planet. Changes in these currents can disrupt marine ecosystems and affect weather patterns.
Impact on Ecosystems
Ecosystems around the world are vulnerable to changes in climate. Global warming is causing significant shifts in the distribution and behaviour of many species, leading to changes in ecosystems and loss of biodiversity.
Habitat Loss and Species Migration: As temperatures rise, many species migrate to cooler areas to survive. However, not all species can move, and those that cannot adapt to the changing conditions face a high risk of extinction. For example, polar bears rely on sea ice to hunt and breed, and the loss of ice habitat due to warming threatens their survival.
Phenological Changes: Global warming also affects the timing of biological events, such as flowering, breeding, and migration. These phenological changes can lead to mismatches between species and their environment, disrupting food webs and ecosystem functions.
For example, early blooming of plants may not coincide with the presence of pollinators, affecting plant reproduction and pollinator populations.
Ecosystem Services: The changes in ecosystems due to global warming can impact the services that they provide, such as clean water, air, and food. For instance, the decline in pollinator populations can affect crop yields and pose a threat to food security.
Increase in Extreme Weather Events
Global warming is associated with a rise in the frequency and severity of extreme weather phenomena, including hurricanes, typhoons, droughts, and floods. These events have devastating effects on human societies and natural ecosystems:
- Hurricanes and Typhoons:
- Droughts and Floods:
- Wildfires:

Warmer ocean temperatures provide more energy for tropical storms, leading to more powerful and destructive hurricanes and typhoons. The severity of these storms leads to more significant damage to infrastructure, increased fatalities, and higher economic expenses. Hurricanes Harvey, Irma, and Maria in 2017 are prime examples of the devastating storms exacerbated by global warming.

Changes in precipitation patterns can lead to more severe droughts in some regions and increased flooding in others. Droughts can cause water shortages, crop failures, and food insecurity, while floods can result in loss of property, displacement of people, and increased health risks from waterborne diseases.
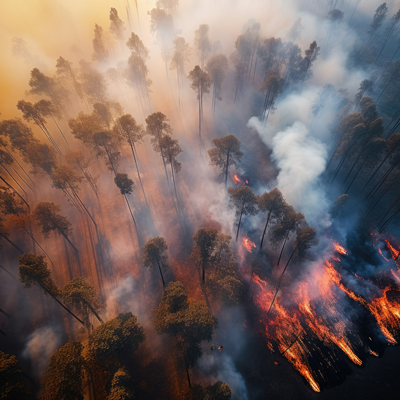

Rising temperatures and prolonged droughts create ideal conditions for wildfires. The frequency and intensity of wildfires have increased in recent years, leading to the destruction of vast forest areas, loss of wildlife, and significant economic costs. The wildfires in Australia in 2019-2020 and the California wildfires are stark reminders of this growing threat.
Conclusion
Global warming is a complex issue that significantly impacts Earth’s climate. The changes in weather patterns, oceanic conditions, ecosystems, and the increase in extreme weather events highlight the urgent need for action to mitigate the effects of global warming.
Addressing this global challenge requires a concerted effort from governments, businesses, and individuals to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, transition to renewable energy sources, and implement sustainable practices. By understanding and addressing the impacts of global warming, we can work towards a more resilient and sustainable future for our planet.
For more such informative/interesting blogs, visit Center Point School.