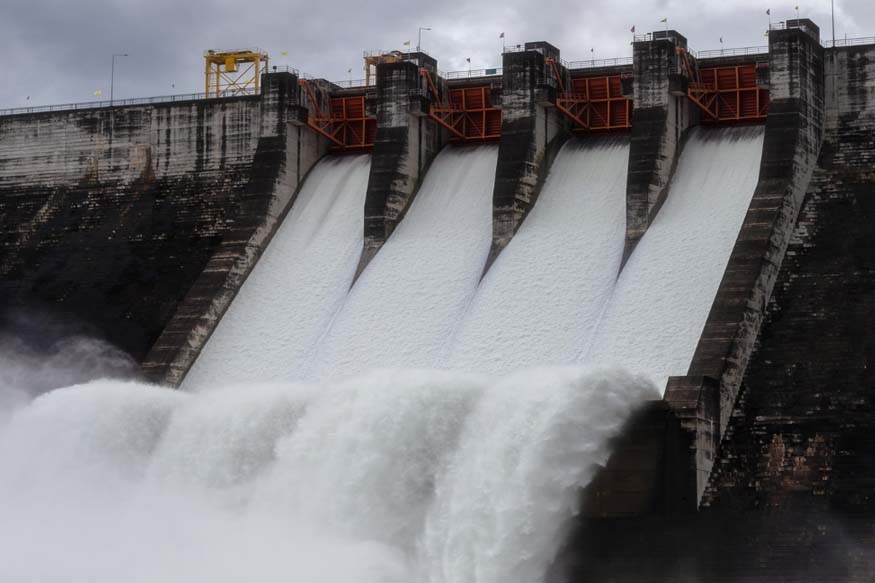
India’s vast and diverse geography has resulted in the construction of numerous dams to manage its water resources. These dams serve multiple purposes, including irrigation, hydroelectric power generation, and flood control for a consistent water supply. The significant number of dams across the country underscores their critical role in India’s development.
As per recent records, India boasts over 5,000 dams that are operational, and several more are under construction. These structures vary in size and function, but collectively they play a crucial role in managing the country’s water resources. The total dams in India are distributed across various states, each contributing to regional water management and agricultural development.
Importance of Dams
Dams are essential infrastructure for any country, and India is no exception. The importance of dams in India can be categorised into several key areas:
Irrigation: Irrigation of agricultural lands is the foremost purpose of several dams across India. Dams provide a stable and controlled water supply, ensuring crops receive adequate water throughout the growing season, thereby boosting agricultural productivity.
Hydroelectric Power: Dams are a major source of renewable energy in India. Hydroelectric power plants harness the energy of flowing water to generate electricity, contributing to the country’s energy needs and reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
Flood Control: Dams help mitigate the impact of floods by regulating water flow during heavy rainfall. They can store excess water and release it gradually, preventing downstream flooding and protecting communities and infrastructure.
Water Supply: Dams ensure a consistent water supply for domestic, industrial, and agricultural use. They store water during the monsoon season and release it during dry periods, maintaining water availability throughout the year.
Recreation and Tourism: Many dams in India are developed as tourist attractions, offering recreational activities such as boating, fishing, and sightseeing. These sites contribute to local economies and promote tourism.
List of Important Dams in India
India is home to numerous dams, each with its unique significance. Here is a list of important dams in India:
Tehri Dam: Tehri Dam is the largest in India, located on the Bhagirathi River in the state of Uttarakhand. This multi-purpose rock and earth-fill embankment dam stands at a height of 260.5 meters (855 feet), making it one of the tallest dams in the world. The Tehri Dam is crucial for irrigation, municipal water supply, and hydroelectric power generation. Its reservoir, Tehri Lake, also serves as a popular tourist destination.
Bhakra Nangal Dam: Bhakra Nangal Dam is one of the highest gravity dams in the world located on the Sutlej River in Himachal Pradesh. It stands at a height of 225.5 meters (740 feet) and serves multiple purposes, including irrigation, hydroelectric power generation, and flood control. The dam’s reservoir, Gobind Sagar is a popular destination for water sports and recreational activities.
Sardar Sarovar Dam: The Sardar Sarovar Dam, located on the Narmada River in Gujarat is one of the largest dams in India in terms of volume and area covered. It plays a vital role in irrigation, drinking water supply, and hydroelectric power generation. The project also aims to address drought and water scarcity issues in Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Rajasthan.
Hirakud Dam: The Hirakud Dam is one of the longest earthen dams in the world and is situated on the Mahanadi River in Odisha. It stretches over 25.8 kilometres (16 miles). This dam’s primary purposes include flood control, irrigation, and hydroelectric power generation. The Hirakud Reservoir provides water for agricultural activities in the region and supports the local economy.
Nagarjuna Sagar Dam: The Nagarjuna Sagar Dam is one of the largest masonry dams in the world, constructed on the Krishna River in Telangana and Andhra Pradesh. It stands at a height of 124 meters (407 feet) and supports irrigation and hydroelectric power generation. The dam’s reservoir is a significant source of water for agricultural activities in the region.
Tungabhadra Dam: Located on the Tungabhadra River in Karnataka, the Tungabhadra Dam is a multi-purpose dam used for irrigation, water supply, and hydroelectric power generation. It stands at a height of 49.38 meters (162 feet) and provides water for several districts in Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh.
Idukki Dam: The Idukki Dam, located on the Periyar River in Kerala, is an arch dam that stands at a height of 168.91 meters (554 feet). It is one of the highest arch dams in Asia and is primarily used for hydroelectric power generation. The dam’s reservoir, Idukki Lake, is a major tourist attraction.
Dams are an indispensable part of India’s infrastructure, contributing significantly to agricultural productivity, renewable energy generation, and water supply management. The list of important dams in India highlights the country’s commitment to utilising its water resources effectively and sustainably. Understanding how many dams in India exist and recognising which is the largest dam in India helps us appreciate the diverse and multifaceted benefits these structures provide.
At Center Point School, we emphasise the importance of understanding and appreciating the role of dams in our country’s development. By learning about the names of the dams in India and the famous dams in India, students can grasp the significance of these engineering marvels and their contributions to society.
Through this knowledge, we hope to inspire future generations to value and protect our natural resources while innovating sustainable solutions for water management and energy production. Recognising the importance of dams is essential for fostering a deeper connection to our environment and ensuring a prosperous future for all.