Nouns are one of the fundamental building blocks of language and communication. We use them to name people, places, objects, and more. Understanding nouns is essential for mastering grammar and enhancing writing skills. In this article, we will explore the definition of nouns, and their various types, and provide plenty of examples to help you grasp their importance and usage.
Definition of Nouns
A noun is a word that identifies a person, place, object or animal. Nouns can function as the subject of a sentence, the object of a verb, or the object of a preposition. Essentially, nouns are the names we give to everything around us, enabling us to communicate clearly and effectively.
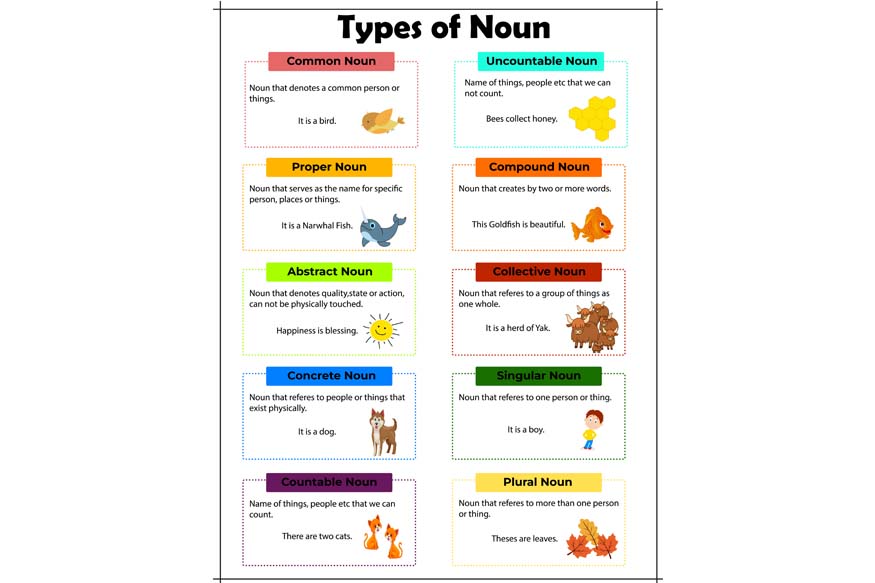
Types of Nouns
Nouns can be categorised into several types based on their characteristics and usage. Let us delve into the main types of nouns:
- Proper Nouns
- Common Nouns
- Concrete Nouns
- Abstract Nouns
- Collective Nouns
- Countable Nouns
- Uncountable Nouns
- Compound Nouns
- Proper Nouns
- Common Nouns
- Concrete Nouns
- Abstract Nouns
- Collective Nouns
- Countable Nouns
- Uncountable Nouns
- Compound Nouns
Proper nouns are specific names of people, places, organisations, and sometimes things. They always begin with a capital letter. Examples include:
People: Maria, John, Dr. Smith
Places: Paris, Mount Everest, Nile River
Organisations: Microsoft, United Nations, Harvard University
Events: Christmas, Independence Day, World Cup
Proper nouns are unique and refer to one specific entity. For instance, “New York” refers to a particular city, not just any city.
Common nouns refer to general items, people, or places. They are not capitalised unless they begin a sentence. Examples include:
People: girl, teacher, artist
Places: city, beach, school
Things: book, car, chair
Animals: cat, dog, elephant
Common nouns can be used to refer to any member of a group. For example, “book” can mean any book, not a specific one.
Concrete nouns are tangible and can be perceived by the senses. They represent physical objects we can see, touch, smell, hear, or taste.
Examples include:
Things: apple, flower, computer
Animals: horse, butterfly, fish
People: child, firefighter, musician
Concrete nouns help us describe the physical world around us.
Abstract nouns represent ideas, concepts, feelings, or qualities the senses cannot perceive. They are intangible. Examples include:
Emotions: love, happiness, anger
Ideas: freedom, justice, democracy
Qualities: honesty, courage, intelligence
Concepts: time, beauty, knowledge
Abstract nouns allow us to discuss complex thoughts and emotions.
Collective nouns refer to a group or collection of people, animals, or things considered as a single unit. Examples include:
People: team, family, jury
Animals: herd, flock, school
Things: bunch, collection, fleet
Collective nouns help us talk about multiple entities as one unit. For instance, “team” refers to a group of players working together.
Countable nouns are nouns that can be counted. They have both singular and plural forms. Examples include:
Singular: apple, book, car
Plural: apples, books, cars
Countable nouns can be preceded by a number or the articles “a” or “an.” For example, “three apples” or “an apple.”
Uncountable nouns, also known as mass nouns, cannot be counted and do not have a plural form. They represent substances, concepts, or collective categories.
Examples include:
Substances: water, rice, air
Concepts: advice, information, knowledge
Qualities: patience, honesty, courage
Uncountable nouns are often used with words like “some,” “any,” “much,” or “a lot of.” For example, “some water” or “much patience.”
Compound nouns are formed by combining two or more words to create a single noun with a specific meaning. Examples include:
Closed compounds: toothpaste, keyboard, basketball
Hyphenated compounds: mother-in-law, six-pack, well-being
Open compounds: bus stop, coffee table, high school
Compound nouns often combine two nouns or a noun with an adjective, verb, or preposition to create a new word with a unique meaning.
Examples of Nouns in Sentences
Let us see how these different types of nouns work in sentences:
- Proper Noun: Emily is going to Paris next summer.
- Common Noun: The teacher gave the students a challenging assignment.
- Concrete Noun: The dog chased the ball across the park.
- Abstract Noun: She felt a deep sense of happiness after achieving her goal.
- Collective Noun: The jury reached a unanimous decision.
- Countable Noun: I bought two new books from the store.
- Uncountable Noun: Can you give me some advice on this matter?
- Compound Noun: We must stop at the gas station on our way home.
Common Challenges with Nouns
Countable vs. Uncountable Nouns: Understanding the usage of “a” or “an” with countable nouns and avoiding these with uncountable nouns.
Example: Correct: “a piece of advice”; Incorrect: “an advice.”
Proper Nouns: Remember to capitalise proper nouns.
Example: Correct: “I visited London.”; Incorrect: “I visited london.”
Plural Forms: Understanding irregular plural forms.
Example: One child, two children.
Conclusion
Nouns are an essential part of speech that allows you to name and describe the world around you. By understanding the different types of nouns you can use them effectively in your writing and communication. Whether you are writing a story, giving a speech, or conversing with someone, nouns are the key to expressing your ideas clearly and effectively.
So next time you write, pay attention to the nouns you use and remember how they shape your sentences and convey your message.
Happy writing!
For more such informative/interesting blogs, visit Center Point School.